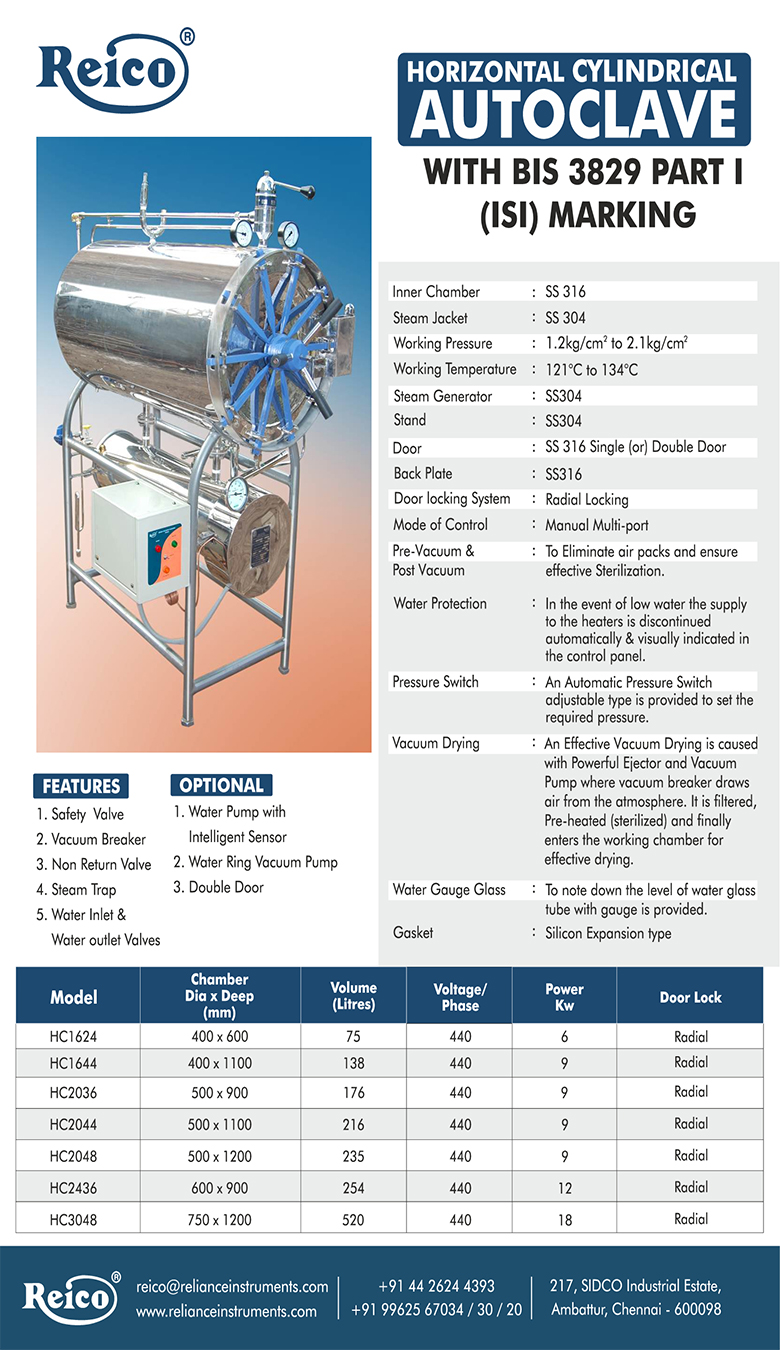
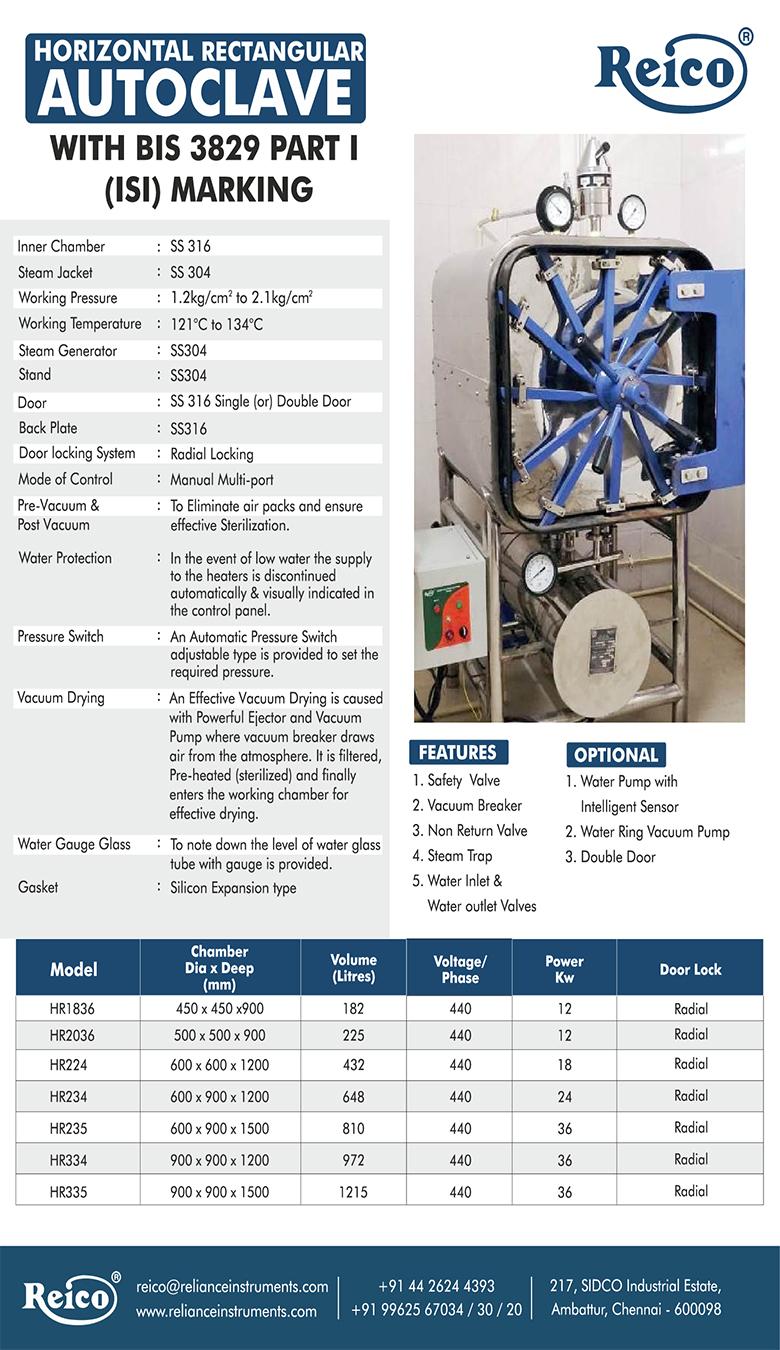
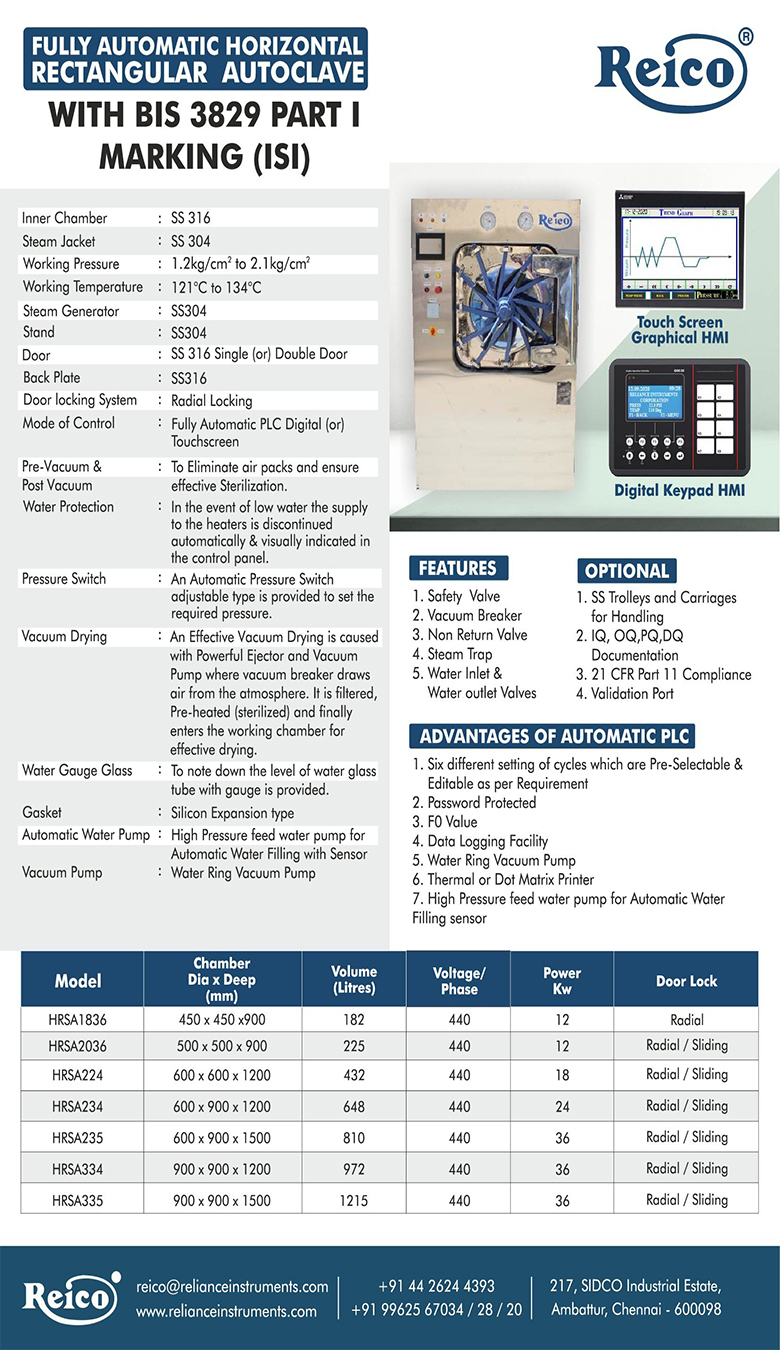
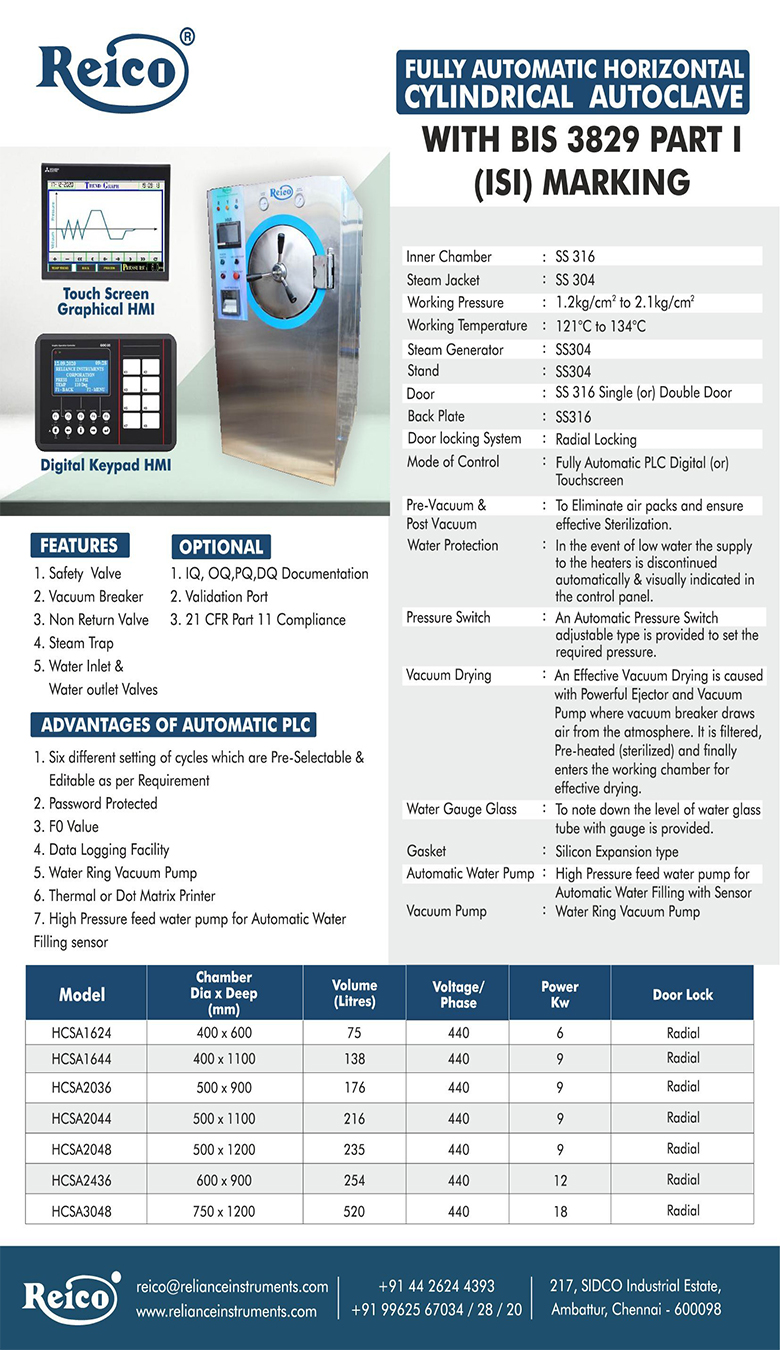
Ethylene oxide (also known as EO or EtO) is a low temperature gaseous process widely used to sterilize a variety of healthcare products, such as single-use medical devices. Through the use of a vacuum-based process, EO sterilization can efficiently penetrate surfaces of most medical devices and its lower temperature makes it an ideal process for a wide variety of materials.
What is Ethylene Oxide Processing?
Ethylene oxide sterilization consists of four primary variables:
Gas concentration
Humidity
Temperature
Time
EO is an alkylating agent that disrupts cellular metabolism and reproductive processes of microorganisms. EO penetrates breathable packaging, making contact with all accessible surfaces of the product to deliver the required sterility assurance level (SAL).
What is Ethylene Oxide Used For?
EO is suitable for the sterilization of a wide range of materials not compatible with other methods of sterilization. Products commonly processed with ethylene oxide include:
Assembled complex devices
Catheters
Custom procedure packs
Equipment with integrated electronics
Multi-lumen tubing products
Stents
Wound care dressings
What are the Benefits of Ethylene Oxide Processing?
Materials sterilized with EO are not exposed to excessive heat, moisture, or radiation. Therefore, a wide variation of materials, particularly polymeric components commonly used in medical devices, can be sterilized with EO. Material compatibility is described in AAMI TIR 17 (compatibility of materials subject to sterilization).
Products can be sterilized in their final packaging, since EO will permeate the sealed films and cartons used to package the device.
Ethylene oxide sterilization uses a 3-part gas process which includes pre-conditioning, sterilization, and aeration